Sen. Colton Moore Attacked & Arrested! 😳
Atlanta, GA — The story is going viral nationwide.
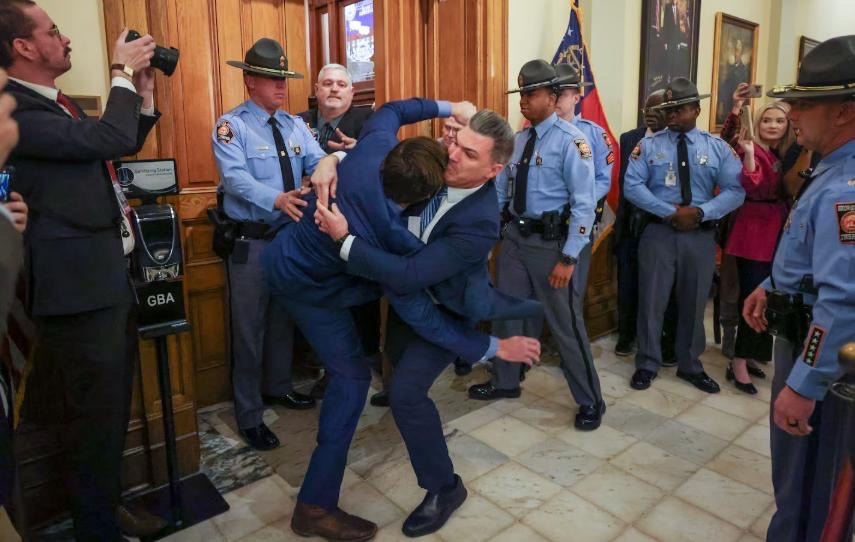
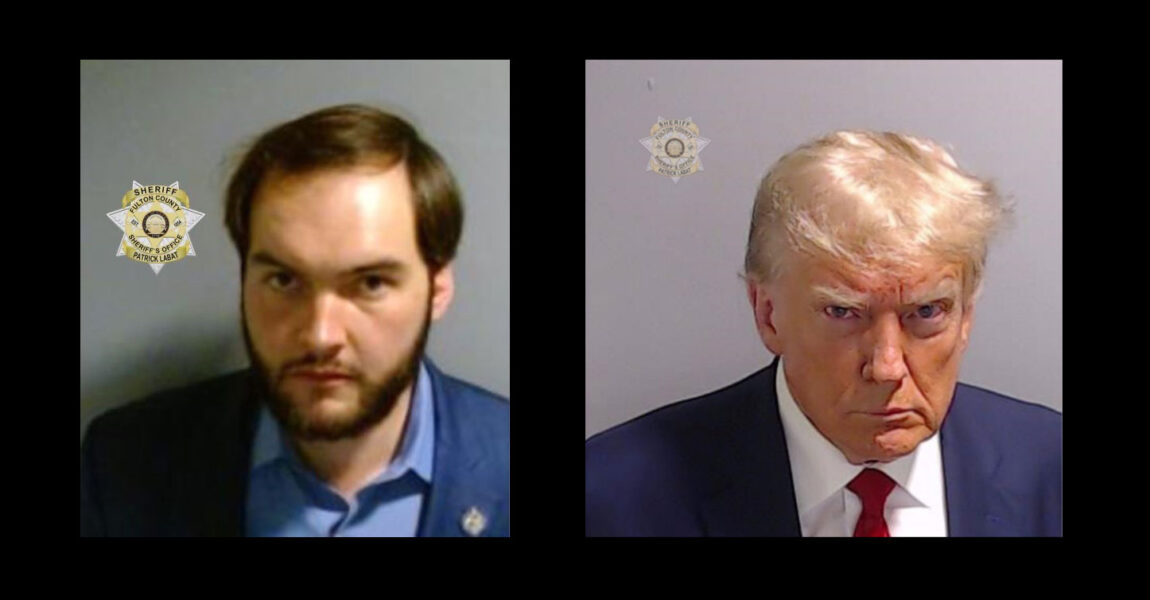
GRA-endorsed State Senator Colton Moore today was illegally blocked from entering a joint session of the state legislature by minions of GA Speaker Jon Burns. The purpose of the joint session was to hear the Governor’s State of the State address. When Senator Moore insisted on exercising his lawful right and duty to attend the joint session, he was wrongfully arrested and sent to the same Fulton County Jail where Donald Trump obtained his famous mug shot.
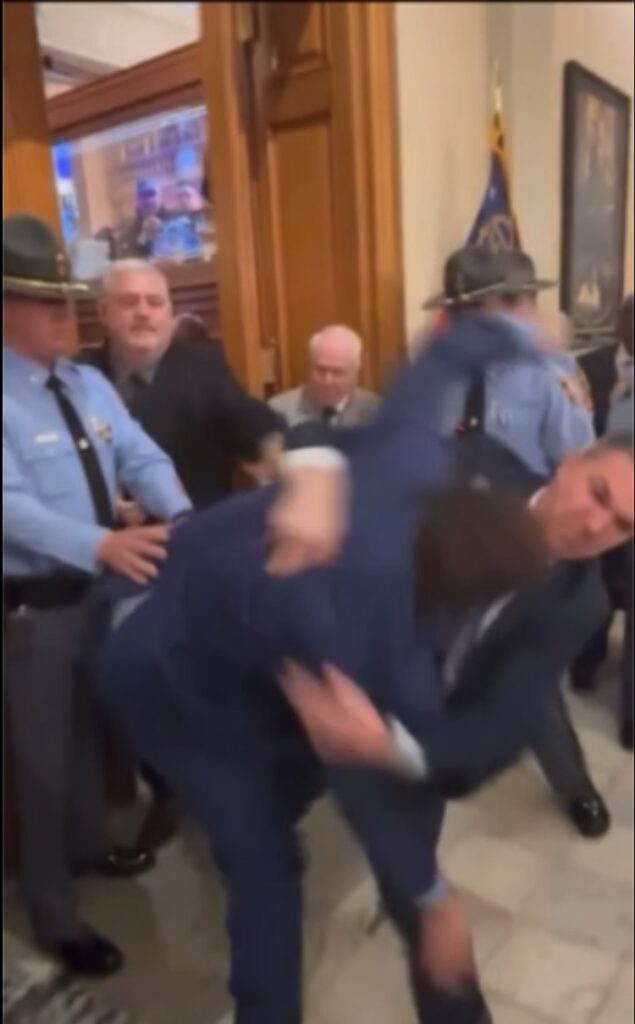

This treatment of Senator Moore was completely unjustified. Both Lt. Governor Burt Jones and GA GOP Chairman Josh McKoon have put out statements acknowledging that fact, but Speaker Burns’ office continues to publicly attempt to rationalize their actions.
If you haven’t yet seen the video of the altercation, you have to see it right away here.
What led up to this scene was likewise petty and tyrannical.
Speaker Burns originally banned Colton from the State House chamber last year when Colton expressed a dissenting opinion about a resolution promoting the late previous Speaker David Ralston. Ralston had a terrible record of corruption, and it was completely inappropriate for him to be put up on a pedestal as a model for other politicians to imitate.
Regardless, however, the Georgia State Constitution explicitly forbids elected state legislators from being treated this way in Article III, Section 4, Paragraph IX, which says:
“Paragraph IX. Privilege of members. The members of both houses shall be free from arrest during sessions of the General Assembly, or committee meetings thereof, and in going thereto or returning therefrom, except for treason, felony, or breach of the peace. No member shall be liable to answer in any other place for anything spoken in either house or in any committee meeting of either house.” (underlining added)

The GRA stands against corruption and cowardice by Republican elected officials. While GRA-endorsed Sen. Colton Moore is willing to let Americans know about the corruption and problems in politics and exemplify courage to uncover and fix them, people like State Rep. Jon Burns and those elected government officials and party officials staying silent exemplify cowardice. They disregard and hate the Constitution. They let people like Donald Trump and Colton Moore go to jail, in hopes they will go away.
To fight against this cowardice and corruption, we need every Republican appalled by this behavior to get involved and join the GRA.
Help us get more true Republicans elected with the integrity and courage of Colton Moore!
The GRA proudly stands 100% with our endorsed State Senator Colton Moore. Our attorney team will support charges Senator Moore pursues against those that assaulted him and obstructed him from performing the duties of his elected office.
We urge you to contact your State Representative and Speaker Burns’ office to register your outrage about how Senator Moore was treated. State Representatives’ contact information can be found at this link. You can call the Speaker’s officer during normal business hours at 1-404-656-5020.
Catoosa GOP Has Grounds to Appeal Federal Association & Speech Case
Rome, GA — Federal Judge Billy Ray yesterday issued his opinion in an attempt to dismiss the Catoosa GOP case brought in federal court. At issue is the Catoosa GOP’s right of freedom of association and free speech under the First Amendment to the U.S. Constitution. This dismissal provides grounds for the Catoosa GOP to appeal, and take the case to the next level in the federal court system for review, and that is exactly what they are going to do!

“In spite of this hurdle,” said Catoosa GOP Chairwoman Joanna Hildreth, “we are going to continue to push this case forward and expect that we will prevail in the end!”
“We applaud the Catoosa GOP for continuing the fight for accountability within the GOP by appealing this dismissal,” said GRA President Nathaniel Darnell. “We feel confident that as this cases moves its way up in the appeals process, closer to the U.S. Supreme Court, the likelihood of the court ruling in their favor rises substantially due to the clear judicial precedent.”
As you may recall, back in March the Catoosa GOP conducted candidate qualifying and they implemented a new procedure that required all candidates wishing to run as a Republican to interview with the party officials to determine if the candidate shared Republican ideology. Four candidates who were incumbent commissioners with a record of raising taxes, restricting the rights of citizens to own chickens, or had endorsed a Democrat, were refused because the local party believed they did not meet the minimum qualification to be called a “Republican.”
Rather than running as Independents or Democrats, the four candidates chose to sue the local party, and a local judge ordered the board of elections to place the candidates on the Republicans Party primary ballot against the will of the party.
Recent SCOTUS precedent on this subject have been unequivocal in protecting the rights of persons and entities in both their associations and their speech. If civil governments can get away with forcing a candidate to be able to run as a Republican, then that opens the flood-gates for violations of other associations. According to the same logic the government could force a Baptist Church to accept a Buddhist or Atheist as an ordained minister in their church. The government could require Coca-cola to have an executive from a corporate competitor like Pepsi on their Board! There is no limit to how association rights could be violated.
In the opinion, this lower court federal Judge here has taken the bait from the attorneys representing the R.I.N.O. candidates and attempted to dismiss the case supposedly on a lack of standing. The reasoning is that since the Catoosa GOP was not supposedly forced to qualify the candidates to run in the Republican Primary, but instead the government forced the BOE to go around the Catoosa GOP and allow them on the Republican primary ballot, that therefore the Catoosa GOP suffered no injury in being forced to associate as Republicans with the candidates.

Most people today consider the old “arranged” betrothal approach to marriage, where guardians selected their children’s marriage partner for them without their consent, as absurd. But that’s what you have here. The reasoning is like saying: “Your right to choose your marriage partner wasn’t violated because you didn’t make the choice on who you would marry. Your guardians made that decision for you.” Huh?
The opinion at least acknowledges that in the Dukes case precedent the state party was allowed to block a candidate from running as a Republican in a federal presidential election, but alleges that this is different here because this case involves counties. Again, huh? So a state party can block a candidate from running for nation–wide office, but a county party cannot block a candidate from running for county office? Based on what line of reasoning? How is that equitable? The judge fails to explain.
Obviously, a county party cannot block a candidate from running for state or federal office. But that is not what we have here. In this case we have a county party operating totally within its jurisdiction to block only county candidates from running as Republicans in the county only.
The opinion furthermore cites a state law in an attempt to use it to super-cede constitutional law. We all know that constitutional law trumps statutory law. O.C.G.A. § 21-2-153 is cited, saying that “all candidates for party nomination in a state or county primary shall qualify as such candidates in accordance with the procedural rules of the their party” provided that the candidates meet the other statutory requirements (emphasis added). The argument the R.I.N.O. candidates’ attorneys have been making from the beginning is that candidates are only required to follow procedural requirements, and may not be subject to substantive requirements (i.e., whether they vote in accordance with Republican policy positions).
This line of argument assumes that substantive requirements and procedural requirements are necessarily mutually exclusive. They are not always. In the case of Catoosa GOP, the elected GOP committee voted to make a substantive review of a candidates’ past performance and messaging as part of the procedural requirements for running in the Republican primary. Procedurally in Catoosa, the county GOP has to vote to approve a candidate before they are allowed to qualify. It is similar to a church or denomination being able to reject an applicant for minister if they find evidence that suggests the applicant does not share their doctrines.
The Republican voters in Catoosa County elected the Catoosa GOP leadership with the power to set such procedures and to review such candidates so that they could inform the low-information Republican electorate in the community (who don’t have time to scrutinize the candidates) whether they will truly represent the minimum standards necessary for the Republican brand. It is a violation of the voter’s rights to steal this protective ability from their elected representatives.
Ballot Questions
The rest of the opinion deals with the ballot questions the Catoosa GOP submitted for the Catoosa Republican Primary ballot. The judge argues that the ballot questions may be blocked in this case because it’s the government who is providing the ballots that the Catoosa GOP is using. The idea is that the ballot questions might appear to be an endorsement of the Catoosa GOP’s speech by the government.
But ballot questions often present messages that are controversial about a plethora of subjects. Allowing the government to start screening and filtering out ballot questions on particular topics means that a government could effectively have the power to block any questions that dealt with something about which the government disagreed.
Support the Catoosa County Republican Party in this law-fare case by donating to their GiveSendGo here: https://www.givesendgo.com/supportjoannahildreth/.
Chris Carr Cops Out & Other Election Integrity Events This Week

The recent opinion issued by the Attorney General’s office is a glaring contradiction to his public statements made just weeks ago. On August 1, 2024, the Attorney General Chris Carr emphatically declared on social media that he would “investigate specific claims of voter fraud” and that his office was ready to “prosecute any voter fraud found in the State of Georgia.” Yet now, he claims that his office is not required to investigate the very fraud referred to him by the State Election Board (SEB), dismissing their request as beyond his statutory obligations.
This about-face is not only hypocritical but also a clear evasion of the responsibilities vested in the Attorney General under Georgia law. O.C.G.A. § 45-15-4 explicitly authorizes the Attorney General to employ private counsel for any branch of state government, including for investigations into matters as serious as election fraud. Additionally, O.C.G.A. § 21-2-31(5) mandates the SEB to investigate election irregularities and report violations to the Attorney General for further investigation and prosecution. The Attorney General’s refusal to act on this referral, especially after publicly vowing to tackle voter fraud, is a betrayal of the trust placed in his office by the people of Georgia.
The Attorney General’s current stance is a deliberate misreading of his role. By refusing to investigate, he is abdicating his duty to uphold the integrity of our elections. The people of Georgia deserve an Attorney General who backs up his words with action, not one who hides behind legal technicalities when it’s time to deliver on promises made to protect our republic.
Some Good News
In other news, in spite of the State Board of Elections Meeting this Monday being made virtual, it turned out to continue to build momentum for election-integrity advocates as the Board voted to pass some additional good rule proposals by their usual 3-to-2 majority.
One key proposal that passed would require county Boards of Elections to reconcile the paper ballot receipt count with the computer tabulators. One would think that this would have already been in place, but it was not.
Even though they were not allowed inside the meeting room at the state capitol, several election integrity advocates still showed up a the capitol to promote the cause.

Georgia Board of Elections Meeting Presents Rays of Hope

Atlanta, GA — GRA members from across the state and other election integrity proponents gathered at the State Capitol Tuesday morning for the State Board of Elections Meeting where cases, public comments, and proposed rule changes were examined. It was also the first meeting where Janelle King, newly appointed from the Georgia House of Representatives, joined the Board, which seems to have had a positive impact. King recently replaced registered lobbyist Ed Lindsey.
An estimated 255 patriots attended, requiring the Board to open two overflow rooms.
Dr. Janice Johnston came into the meeting swinging from the very beginning, making a motion to revisit the Rossi case. The Chair held that motion out of order, and Dr. Johnston immediately appealed the decision of the Chair. That led to the Board going into executive session to deliberate. When the Board came back into the public forum, Rick Jeffares joined with the Democrat-appointed member of the state Board and the Governor’s appointed member Chairman John Fervier to block the effort. Off to that rocky start, things began to get better as the day progressed.
Garland Favarito was given 15 minutes to expound on concerns related to the Rossi case, such as, thousands of missing ballot images, ballots that appear to have been counted twice, and Fulton County’s unwillingness to comply with Open Records Requests to examine the actual ballots. He graciously and succinctly laid out a persuasive case for the Board and then introduced other elections experts who would also testify to the problems. According to expert computer technician Patrick Parikh, there is a loss of “SHA files” related to the meta-data in the Dominion voting machines that make them dubious and vulnerable to hacking.
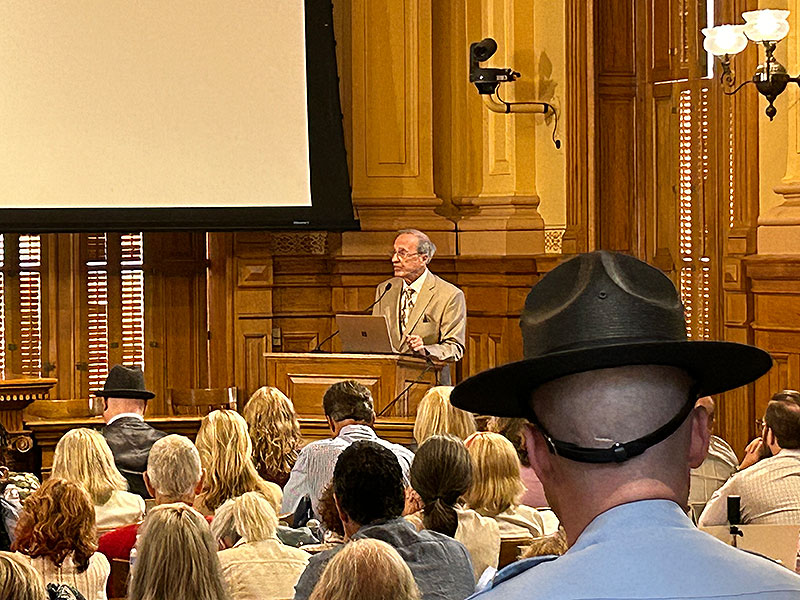

The public comments were overwhelmingly favorable to election integrity. Over 50 people had signed up for public comment at two minutes each. Sam Carnline, Jason Frazier, and Matt Rowenczak were among them. GRA member Holly Kessler from Savannah reported, “There is a pattern of manipulation. … I have the Ware County duplicates. … We are going into the most critical times of elections in our lives. It’s up to the [Board of Elections] to figure this out. We do support you, but we are asking you to step up and do the right thing!”
GRA member Tim Talbot from Gainesville said, “You need to act!”
Janelle King asked one of the commenters opposing election integrity reform whether saying an election was “certified” means that an election “happened” or if it means the election was “correct.”
Cobb RA member Salleigh Grubbs (the Chairwoman of the Cobb GOP) won a solid victory on a rule proposal she presented before the Board in the afternoon. Salleigh’s proposal would have clarified that before local county Boards of Elections certify an election, they must first examine irregularities or inconsistencies to make sure the election was conducted accurately. So, for example, if the number of ballots cast is different from the total number of votes, this would be investigated and corrected before finalizing the report of the election results in a precinct or county.
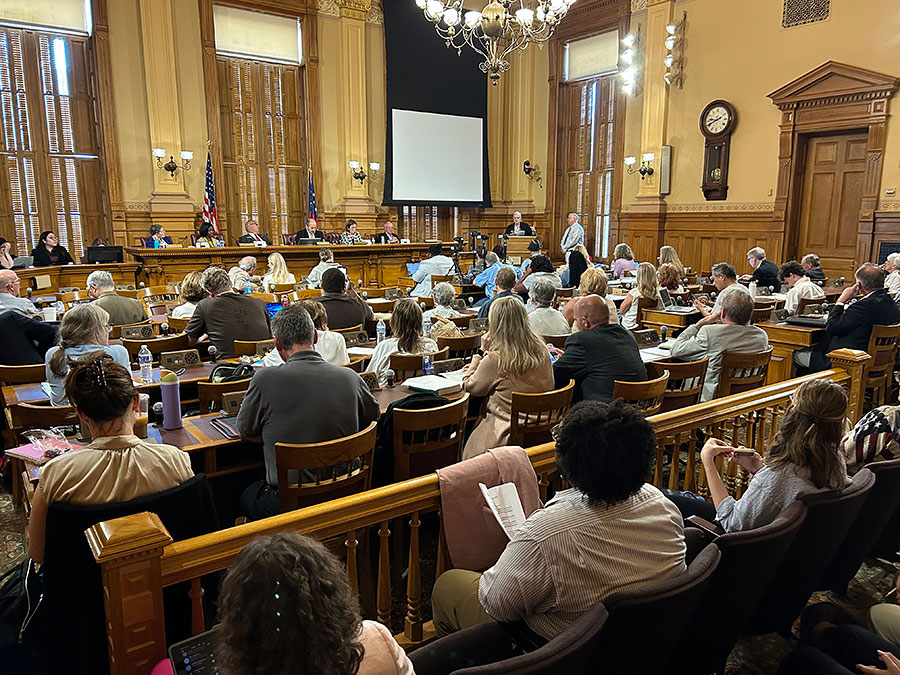

Chairman Fervier objected to Salleigh’s proposal, saying that it conflicted with a proposed rule change he had on the agenda. Salleigh replied to him with a polite smile, “I like my rule better than yours.”
Dr. Johnston expressed concern that the “guidelines” in Fervier’s proposal would create more restrictions on accountability. “It’s already too complicated,” added Janelle King.
After much discussion, when the Board voted on Salleigh’s proposal, Rick Jeffares (nominated by Lt. Governor Burt Jones) was the third vote in favor of Salleigh’s proposal. King and Johnston also voted in the affirmative.
The packed room exploded in applause with that win.
Rising Tide of Lawfare Against Conservatives: A Call to Action
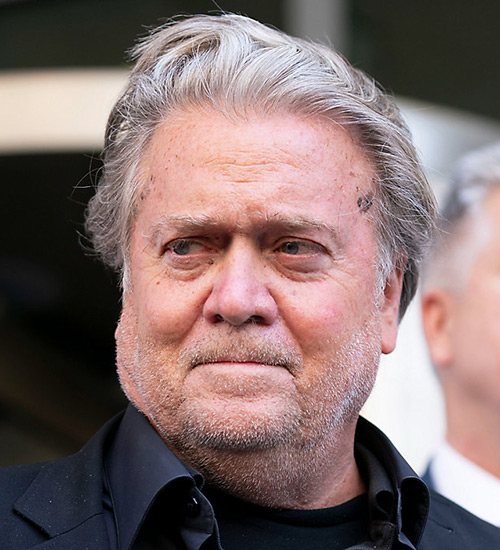

In the last 24 hours, we have witnessed two more instances of unprecedented lawfare targeting right-wing figures. Steve Bannon faces imprisonment, while Dr. Eithan Haim, who blew the whistle on Texas Children’s Hospital’s illegal child sex-change program, is now being prosecuted by Joe Biden’s DOJ on what many see as outrageous and trumped-up charges.
America is increasingly polarized and divided, with Democrats driving this divide through unjust legal actions across our nation. This situation is further exacerbated by the cases in Georgia and Arizona against alternative slates of electors, which hold significant weight in both legal and political history.

The prosecution of Donald Trump across multiple states is a glaring example of the corruption and political bias infiltrating our justice system. In New York, the former president faces charges stemming from what many consider a politically motivated investigation into his business dealings. In Georgia, Trump and his associates are entangled in a case driven by partisan interests, targeting alternative electors in an unprecedented move that undermines the democratic process. Meanwhile, in Florida, Trump is contending with allegations related to classified documents, further showcasing the relentless legal assault aimed at derailing his political career. These cases collectively illustrate a concerted effort to weaponize the legal system against a prominent conservative figure, underscoring the urgent need for Republicans to unite and fight back against these corrupt practices.
As the Georgia Republican Assembly, we call on Republicans from across the nation to unite around our presumptive presidential nominee, Donald Trump. It is crucial to take the fight to the Democrats by organizing, mobilizing, and electing true Conservative politicians who will combat these corrupt abuses at the local, state, and federal levels.
Together, we can stand against the misuse of the legal system and uphold the principles of justice in America.
Read about the Steve Bannon story:
https://www.theblaze.com/news/federal-judge-orders-former-trump-advisor-steve-bannon-to-prison
Read about the Etithan Haim story: https://www.givesendgo.com/texas_whistleblower
Catoosa GOP Finally Gets Heard In Federal Court
Rome, GA — Wednesday, federal Judge Billy Ray heard arguments from the Catoosa GOP that the Catoosa Board of Elections acted unlawfully when they followed state Superior Court Judge Don W. Thompson‘s order to violate the Catoosa GOP’s 1st Amendment protected right to freedom of association by forcing four known RINO candidates onto the Republican primary ballot. These candidates have a record of implementing democrat policies (like raising taxes, prohibiting property rights, etc.) and opposing basic tenants of the Republican Party platform. For the first time, attorneys for the Catoosa GOP were allowed to present their legal arguments in the courtroom since Judge Thompson had precluded any oral arguments on the merits of the Catoosa GOP’s position in his courtroom in Ringgold.
At issue is whether private organizations (such as political parties, businesses, clubs, or churches) have the right to freely associate or disassociate with someone who does not share the standards of that private organization. Recent SCOTUS precedent on that question says political parties do have that right, according to the Catoosa GOP.

Unlike the courtroom in Ringgold, the federal courtroom in Rome hearing this case was not covered in police officers or following unusual measures in an effort to intimidate. Indeed, the federal courtroom did not appear to have a single officer in the room. Federal Judge Ray adopted a very inquisitive posture, asking numerous questions of attorneys, coming at the controversy from many angles, and musing aloud regarding the implications of different legal positions.
Judge Ray mentioned in the proceedings that the threats of jail time and exorbitant $1,000 per hour fines against the Catoosa GOP Executive Committee members that were imposed by Judge Don W. Thompson should, it seemed to him, no longer apply since that was from a civil case and the plaintiffs have already obtained their desired remedy. Time will tell if other judges in on-going proceedings agree with Judge Ray on that point.
“The crux of this case is really questioning the very essence of a political party,” said GRA NFRA Director Abigail Darnell. “If a political party plays nothing more than a superficial administrative role, rubber stamping every candidate with no regard to their beliefs or their record on public policy, then why have a political party at all?”

Attorneys Alex Johnson and David Oles (also the 11th Congressional District Chairman) were on hand to represent the Catoosa GOP, and Catoosa County government attorney Christopher Harris represented the Catoosa Board of Elections members. Harris also represents the county commissioners — three of which are also among the four rejected candidates — which, as an employee of the county, paid by those commissioners, appears to be a conflict of interest.
Harris made the argument that the Catoosa GOP procedures for vetting and qualifying candidates were “inconsistent” with the GA GOP state party rules. Attorney Alex Johnson pointed out that there is no “inconsistency” because the GA GOP State Party rules do not address county processes on this point, and certainly do not preclude county party’s vetting and refusing to qualify candidates who don’t demonstrate a track record of faithfulness to Republican Party platform principles. The Catoosa GOP rules, including the new accountability measures and candidate vetting process, were unanimously approved by the delegates at the Catoosa GOP County Convention after the rejected candidates filed their lawsuit.
Harris also argued that such an Accountability Rule was rejected by the GA GOP State Convention last year. When Judge Billy Ray asked attorney Alex Johnson about that event, Johnson pointed out that he was actually the delegate at the convention who had submitted the proposed Accountability Rule last year, and that that proposed Accountability Rule had nothing to do with county party organizations. He also pointed out that the rule was never actually allowed to be voted on at the convention since it was blocked in committee and the convention chairman did not allow the proposal to be brought up from the floor.

Far-left newspaper Atlanta Journal Constitution reporter Greg Bluestein was in the federal courtroom observing and incorrectly reported yesterday that Johnson’s proposed Accountability Rule would have given the GA GOP the power to reject candidates to state office. In actuality, the GA GOP already possesses the constitutional authority to reject candidates under the freedom of association — and has recently done so for the presidential ballot last year as well as for former K.K.K. clansman David Dukes when he attempted to run for president as a Republican in 1992. The proposed Accountability Rule from last year would have only provided a process for the delegates at a state convention to vote on potentially blocking a state candidate from running for future office as a Republican instead of that authority being seen as exclusively the domain of the GA GOP 28-person Executive Committee or the 180-person State Committee. According to the Call of the GA GOP, the state convention has a capacity this year of 2,641 delegates.

Federal Judge Ray allowed Johnson to chronicle how Judge Don W. Thompson had called an ex parte hearing with little notice to the attorneys on the Tuesday morning the week of candidate qualifying, and did not allow attorneys to present oral arguments on the First Amendment issue of right of association. Johnson delved deeply into the extensive case law from the United States Supreme Court which repeatedly applies that legal right specifically to political parties.
Judge Ray asked Johnson about the interplay between state law specifying the procedure for how candidates are qualified and the U.S. Constitution in the 1st Amendment. Attorneys for the four RINO candidates have argued that the state law does not specify that political parties have any discretion over qualifying candidates who appear and follow the process. Johnson argued that the state law must be seen to be in conformity with the First Amendment and not in conflict with it. If somehow the state law did prohibit freedom of association, Johnson pressed, the 1st Amendment from the U.S. Constitution must have supremacy over state law. “That’s what the Civil Rights movement was all about,” Johnson said.
The Catoosa GOP’s county committee voted unanimously to adopt the procedures in their organization’s rules for vetting and qualifying candidates. The members of that committee are elected every two years by the local activists in Catoosa County, and serve as the representatives of the Republican voters in that county. They are responsible for guarding the interests of the local Republican Party, says the Catoosa GOP, including upholding minimum standards of quality that Republican voters can rely on when they go to vote in the primaries. Approving a candidate for qualifying as a Republican operates as a stamp of approval that voters, who cannot often pay close attention to local government operations, can rely.
Catoosa GOP’s Muzzled Ballot Questions

The hearing on Wednesday also addressed ballot questions the Catoosa GOP had submitted to the Catoosa Board of Elections to be included on the Catoosa Republican Primary ballot. Some of those questions inquired about voters’ awareness of the candidate qualifying controversy, and awareness of public votes of the County Commission and were not an example of defamation. County attorney Harris said that the Secretary of State’s office had told the local BOE to refuse to use the questions because, they argued, they were illegally “electioneering.” However, Harris admitted “in candor to the court” that the Secretary of State’s office called him and said they are no longer claiming the ballot questions are “electioneering” and that the decision rested solely with the Catoosa Elections Board. Judge Ray pointed out through his questions that the statute prohibiting “electioneering” says no “person” shall engage in that activity, and neither a printed ballot nor a voting machine are a legal person under that statute. He also said that the statute relating to qualifying questions from political parties says they “shall” be posted and do not give the Board of Elections much discretion on whether to post questions submitted or not.
“This is yet another atrocious example of bias and discrimination against the Catoosa GOP,” said Abigail Darnell. “If this illegal action is allowed to stand, it will demoralize GOP activists and discourage party participation across the state. I mean, why would I want to give unpaid volunteer hours to an organization just to be strong-armed by the government? Party activists shouldn’t be forced to conform to a government-approved message or government-forced association.”
Time is Ticking
The ballots will soon be finalized for the upcoming primary election in May.
Federal Judge Billy Ray pointed out that he has particular experience in the subject matter of the case since he was formerly a Republican State Senator from northeast Georgia from 1996 to 2002, so he was familiar with candidate qualifying procedures, and he had also formerly been a Gwinnett County GOP officer responsible for qualifying candidates. In 2002, Ray was appointed to the state superior court by out-going Democrat Governor Roy Barnes. Ten years later he was appointed by Republican Governor Nathan Deal to the Georgia Court of Appeals. In 2018, he was appointed by former President Donald Trump to the federal District Court for Northern Georgia.
Judge Ray cautioned at the conclusion of the proceeding that he would not be making any promises on how quickly he would decide on this case. He made it clear he did not want to be rushed, even though he was mindful that the ballots would soon be printed for the Catoosa Republican primary election in May. He also pointed out that even if the four candidates do end up on the ballot, the Catoosa GOP could still pursue monetary damages.
Four Judges Recuse from Catoosa GOP Qualifying Case as It Heads for Appeal

Ringgold, GA — Tuesday the four local judges in the Lookout Mountain Judicial Circuit filed to recuse themselves from the case in Catoosa in which four candidates are trying to use the civil government to force themselves on the Republican Primary ballot. We are pleased to report that the appeal is moving forward, and the Catoosa GOP is committed to continue fighting for the constitutional right to freedom of association. The government does not have the constitutional authority to force a private entity such as a political party to publicly associate with someone who does not represent their values.
We applaud that Judge Thompson and the other three judges on the Lookout Mountain Judicial Circuit who have recused themselves to ensure this case can be given fair and unbiased consideration.
14th District GA GOP Chairwoman Denise Burns lives in Catoosa County, and interviewed with local television news about the story, which you can see here:
Last Saturday the Catoosa County GOP hosted one of the largest attended county conventions in recent history and if any Republican voters had concerns about the Catoosa GOP leadership, they did not show up at the convention to express it. The unity and enthusiasm in the room was unmistakable. None of the people trying to force their way on to the Republican Party ballot or their alleged supporters were in attendance. We are glad to see the unified support from Republicans in the Catoosa community to only have Republicans on the Republican primary ballot.
The Catoosa GOP Convention unanimously passed the a resolution in full support of the Catoosa GOP leaders in their fight for freedom of association.
Next Tuesday, the Catoosa Board of Elections will be holding a hearing at the Catoosa County Courthouse to hear from local citizens who have filed challenges to the four candidates being forced onto the Republican primary ballot. That hearing is expected to start at 9:00am.
Senator Colton Moore Banned by Speaker Burns After Speaking the Truth about Ralston
You may recall that our GRA-endorsed State Senator Colton Moore (R-53) was the only Senator calling for a special session to get rid of Fulton Democrat DA Fani Willis. He proposed a bill to change the RICO law to end the Fulton prosecutions. And as a reward for it, he was kicked out of the Republican caucus by our “Republican” politicians.
And just this week, on Legislative Day 35, during a debate to name a government building after the late Former House Speaker, David Ralston, Sen. Moore had this to say.
Note that Sen. Moore was pointing out information, and didn’t even delve into the anti-Republican tactics used throughout the years that were discussed in past Advance the GOP messages.
The response from the Establishment was, again, excessive.
Immediately leaked to the liberal media and banning him from the House floor with articles lacking details. And then the Establishment politicians, many of whom had previously feared Ralston, continue to hypocritically sing his praises.
And then the Establishment, throughout social media, push the shaming narrative that it wasn’t “the time and place” for a Senator to bring up the reasons to NOT name a government building after a politician, during the debate on naming the building after the politician.

The hypocrisy and lies are mind-blowing.
Yet they keep happening. Over and over again.
Why?
YOU – YOU ARE THE PROBLEM – AND SOLUTION
I know you don’t want to be the problem. I didn’t want to be either. But the reason why the Establishment keeps doing this, and getting away with it, is because we don’t stand up. We don’t share this information.
We don’t have the time. Or we’re afraid it’ll offend our neighbors and friends. Or we’re afraid that all the politicians will come after us.
The Establishment tries to keep us afraid.
Like they did with the Catoosa GOP.
Like they are doing with Sen. Colton Moore.
Catoosa Judge Backs Off of Forcing the County GOP to Qualify RINO Candidates
Ringgold, GA — In spite of severe threats to intimidate and coerce, none of the brave Catoosa GOP leaders were forced to spend time in jail as a result of their refusal to obey an unlawful order from a local judge attempting to force them to qualify RINO candidates. For the third time this week, Judge Don W. Thompson‘s bias was on full display this morning as he refused to let the Catoosa County GOP present any oral arguments in legal defense of their decision not to qualify these candidates as Republicans in the Republican Primary for county commissioner. The first courtroom hearing was held at 9:00 am Tuesday morning, but the Catoosa GOP’s attorneys were not made aware of the first hearing until it had already happened. The judge at that time ordered the Catoosa GOP to allow the candidates to qualify as Republicans in the primary.

No one was preventing them from running as a Democrat, third-party, or Independent. They were simply denied the Republican label. The Democratic Party of Chattooga County rejected a candidate seeking to run as a Democrat commissioner back in 2014, thereby setting a precedent for this decision.
The Catoosa GOP had previously adopted a rule that invites candidates to be interviewed, and their voting records in office examined, along with their public statements, prior to the members of the Executive Committee holding a vote to qualify. The votes were cast by secret ballot. Those who were allowed to qualify were issued affidavits, in accordance with the rules of the local party. In the view of the majority of the members of the Catoosa GOP Executive Committee, four candidates, with a voting history from previously serving on the county commission, advanced several policies contrary to the principles and policies specified in the Republican Party platform. The four candidates are Vanita Hullander, Jeff Long, Steven Henry and Larry Black.
“When you do things such as pass two tax increases, pass restrictions on citizens’ raising chickens on their private property, publicly endorse a Democrat, and tell folks that they can only get their freedom back if they get a COVID vaccine,” said GRA President Nathaniel Darnell, “you shouldn’t be surprised when the local GOP leadership considers you a RINO and doesn’t want to re-qualify you to run as Republican with their stamp of approval.”
While these candidates complained that the Catoosa County GOP leadership was trying to help their favored candidates, that accusation was disproven when the Catoosa GOP qualified two or more candidates for the same race for various seats. The Catoosa GOP clearly stated, “The Catoosa County Republican Party proudly welcomes all county citizens who share our common conservative values and support our Republican principles.”

Judge Thompson held a second hearing at 1:00 pm Thursday, but again the judge refused to allow the Catoosa GOP’s attorneys to present oral arguments. Instead, the judge only allowed the attorneys for the complaining candidates to cross examine Catoosa GOP Chairman Joanna Hildreth on the witness stand. Three of their five attorneys took turns hammering her, demanding that she identify the names of the other members of her Executive Committee, and asking how she personally voted in the secret ballot. One attorney accused her of “celebrating” the denial of the candidates at her monthly county GOP meeting Monday evening, even though the matter never was mentioned at all there.
At the conclusion of that second hearing, Judge Thompson offered to let the attorneys for the Catoosa GOP call for other witnesses. When attorney Catherine Bernard said they had no other witnesses, the judge proceeded to give his ruling. Bernard attempted to interject, asking why they had not been given an opportunity to present closing oral arguments on the legal merits of their client’s position. The Judge said he was in the middle of his ruling, and would not be interrupted.
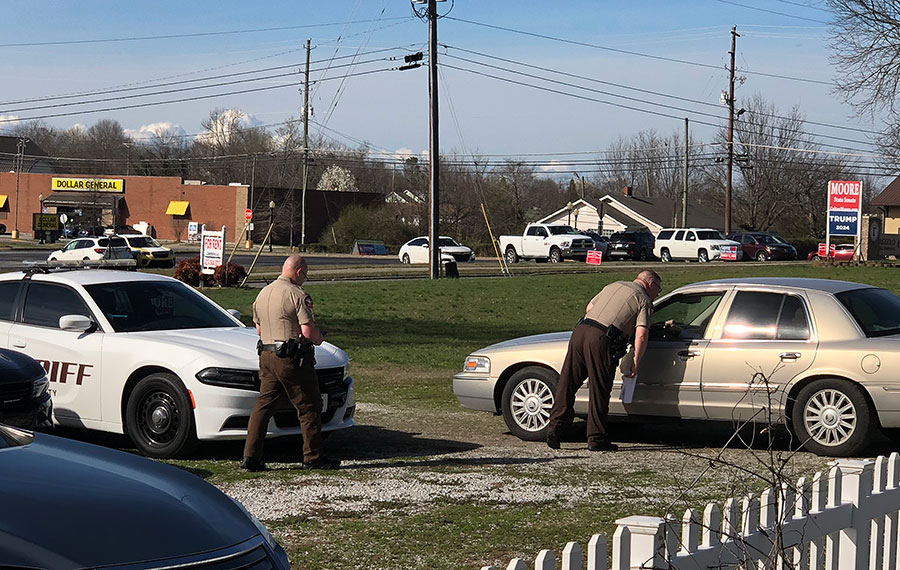

He doubled-down on his order to the Catoosa County GOP, specifying that each of the six members of the Catoosa GOP Executive Committee would be fined $1,000 per hour for each of the four rejected candidates, and face up to 20 days of jail time, until the candidates were allowed to quality as Republicans in the primary. Yes, these courageous GOP volunteers were staring jail time in the face, all for standing on the constitutional right of freedom of association, that says government may not force a private entity to associate with someone against their will. He also specified that two police deputies wearing body cams would accompany the candidates as they attempted again to qualify.

As he was concluding Thursday, the Judge remarked to the attorneys for the RINO candidates that he didn’t think the Catoosa GOP would comply, and so he asked if they had any other remedies that could be pursued. Attorney Bryan Tyson replied that there was no other way they could qualify apart from the Catoosa GOP complying because state code O.C.G.A. § 21-2-153(c)(2) specifies the local board of elections office can only qualify if a three-day notice requirement is met, but there was only one more day left to qualify.
After the second hearing adjourned, the four candidates did attempt once again to show up at the Catoosa GOP qualifying office and demand to be approved. They were accompanied by the police deputies. The volunteer notary on duty said she could not allow them to qualify without the affidavit required by the rules.

Since their effort to intimidate the GOP leaders failed, Tyson and the other opposing attorneys showed up Friday morning in court in Catoosa and contradicted their admission from the previous day that they had no recourse to go around the county party. The Judge ruled in favor of that approach, and told the opposing counsel to draft the order, and let him approve it for issue. The written order admits that they are violating the notice requirements in the state code, but alleges that they have no choice but to break the law.
Many wondered if any of the Catoosa GOP leadership would be arrested at the third hearing. No arrests were ordered, but a new hearing has been scheduled for March 27th.
Before the written order had been drafted, approved by the judge, and issued for the Catoosa GOP to be able to respond with any contrary motions, the local elections superintendent had already acted to qualify the the complaining candidates. It is yet to be seen whether a majority of the Catoosa Board of Elections will vote to approve the qualifying as Republicans in the primary or deem it to be against the law. If they do approve, then there will be other legal remedies available. The Catoosa GOP pledged to continue to work with their legal counsel to appeal Judge’s Thompson’s order and take the case before a different court.
Support the Catoosa County Republican Party in this law-fare case by donating to their GiveSendGo here: https://www.givesendgo.com/supportjoannahildreth/.